VEST I
A Randomized Trial of External Stenting for Saphenous Vein Grafts in Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
Study design & primary objectives
NCT01415245 (clinicaltrials.gov reference #)
Trial period: Oct/2011 - Sep/2013
Sample size: N = 30
Participating centers:
- John Radcliffe, Oxford, UK
- Royal Brompton, London, UK
- Harefield, London, UK
Principal investigator: Prof. David Taggart, Oxford, UK.
Design:
First-in-Man, prospective, multicenter, randomized, self-controlled study. The study was designed to demonstrate the safety efficacy of VEST in mitigating intimal hyperplasia and maintaining vein graft lumen uniformity at 1 year, as compared to the unsupported vein grafts.
Primary Objectives:
Comparison analysis for intimal hyperplasia area as assessed by IVUS at 12M.
Comparison of QCA (Quantitative Coronary Angiography) variables related to vein graft disease and failures such as lumen ectasia, lumen uniformity and flow pattern.
Results summary
Mitigation of intimal hyperplasia:
14.6% - 27.4% reduction in overall intimal hyperplasia area and thickness in VEST supported SVG at 1 year compared to control SVG (p<0.05).
SVG Patency Rate at 1 year:
- Overall VEST supported SVG; 70%
- VEST supported -SVG with no metal clips 82%
- Control SVG group; 71%
SVG Patency rate at 1 year by territory (VEST vs Control):
- Left territory: 82.4% vs 72.5%
- Right territory: 54.8% vs 86.6%
Metallic clips were found to be the main trigger for VEST SVG failure in the right coronary territory prompting the VEST II trial.
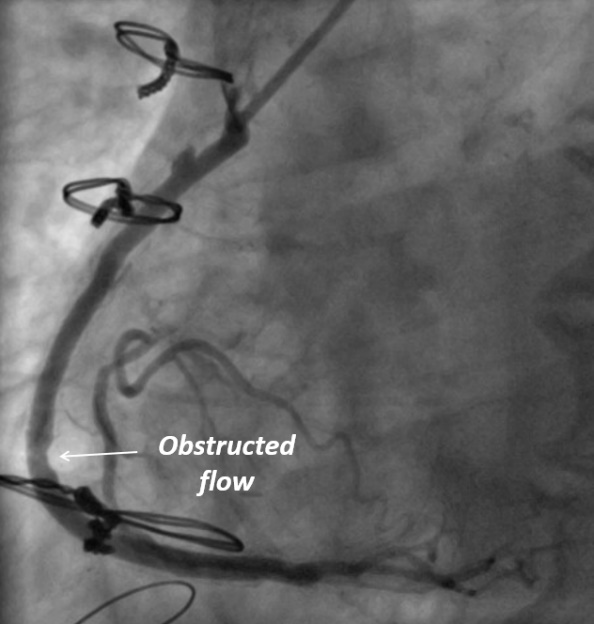
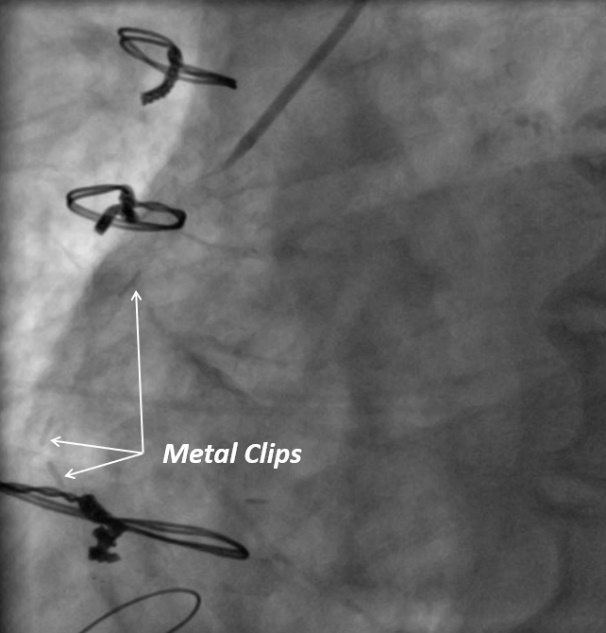
Lumen Uniformity:
The lumen of the stented SVG was more homogeneous (the difference between maximum and minimum lumen diameter was significantly smaller in stented compared with non-stented grafts, 0.28+0.19 vs. 0.33+0.23 mm, respectively, P=0.006), and more circular (mean eccentricity index 0.08+0.06 vs. 0.10+0.06, supported vs. unsupported; P=0.019).
Flow Pattern:
Oscillatory Shear Index (OSI) was significantly lower in stented versus Non-stented SVG group (P= .009), respectively, and was directly related to the reduction in intimal hyperplasia.
Thrombus Formation:
- VEST supported SVG; 0%
- Control SVG; 13%
Main Conclusions
1. VEST support technology significantly reduces intimal hyperplasia, the dominant SVG pathology, compared to both control and historical data.
2. Patency rates of VEST supported SVG’s at 1 year are comparable with control SVG’s and historical data, and trending toward improved patency when used without metallic ligation clips.
3. VEST prevents SVG remodelling at 1 year assessed by the development of lumen irregularities and deformation.
4. VEST significantly improves SVG flow hemodynamics and reduce thrombus formation
VEST I Publications
Name |
Link |
Randomized Trial of External Stenting for Saphenous Vein Grafts in Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting |
|
Flow patterns in externally stented saphenous vein grafts and development of intimal hyperplasia |
|
Numerical analysis of Venous External Scaffolding Technology for Saphenous Vein Grafts |
